Spine Surgery
Scope of Endoscopic Spine Surgery
- Transforaminal Endoscopic Discectomy
- Interlaminar Endoscopic Discectomy
- Percutaneous Stenoscopic Lumbar Decompression(PSLD)
- Endoscopic Lumbar Fusion
- Endoscopic Thoracic Decompression
- Endoscopic Cervical Discectomy
- Endoscopic Cervical Foraminotomy
- Endoscopic Debridement for Discitis
- Endoscopic Drainage of spinal Epidural Abscess
- Endoscopic Excision of Spinal Tumor
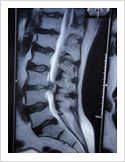
Disc Prolapse
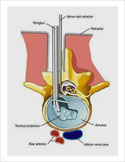
Endoscopic Disc Surery
This is the latest, least invasive and most advanced procedure for disc prolapse causing sciatica. It is done under local anaesthesia. For details, see keyhole disc surgery.y
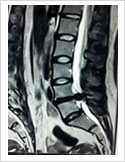
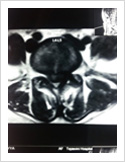
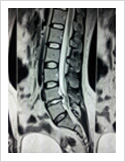
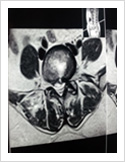
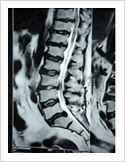
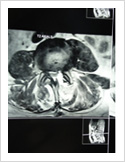
Micro Discectomy
This surgery is done for disc prolapse when endoscopic surgery cannot be performed. In this procedure, 3-4 cm long skin incision is made over the posterior midline; para spinal muscles are elevated on one side. A small window is made in the lamina (bone) and herniated disc is removed. This procedure is done under spinal or general anaesthesia. Patient needs to stay in the hospital for 3-4 days.
Spinal Stabilisation And Fusion
In patients with longstanding disc prolapse and significant back pain, patient may require spinal stabilisation and fusion. In this surgery, pedicle screws are inserted into the vertebra, disc is completely removed, and disc space is filled with bone graft and titanium cage.
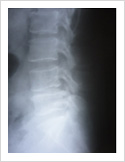
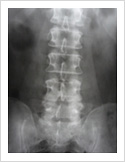
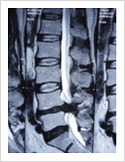
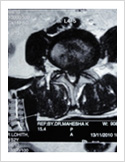
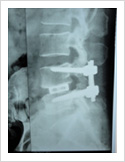
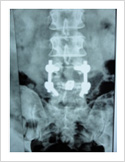
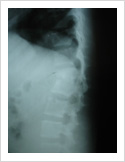
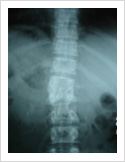
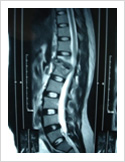
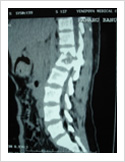
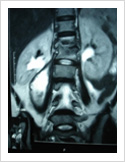
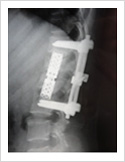
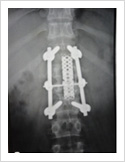
Tuberculosis of Spine
Tuberculosis can affect the spine causing pain, pus formation, destruction of the vertebra and neurologic deficit. Most of these patients can be treated with antitubercular medicines, rest and bracing. However, if the patient comes late with neurologic deficit, instability, failed conservative treatment, they may require surgery. Surgery involves stabilisation with pedicle screws, drainage of abscess and fusion with or without cage.
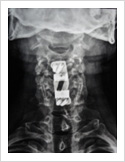
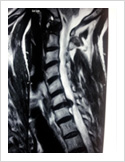
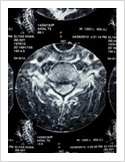
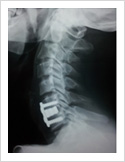
Cervical Disc Prolapse
Cervical disc can herniate causing pain in the neck, upper limb pain, numbness and weakness. Majority of these patients respond to conservative treatment. If the patient fails to improve after six weeks of conservative treatment, surgery may be required. Surgery involves removal of the disc and fusion with plate and screws.
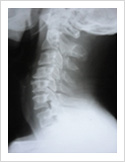
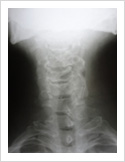
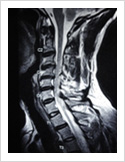
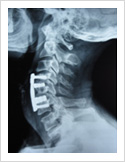
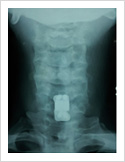
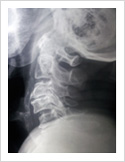
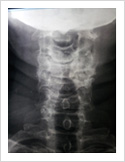
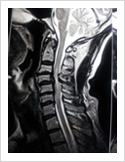
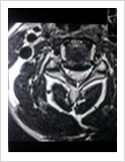
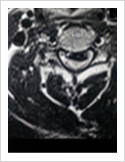
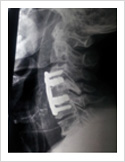
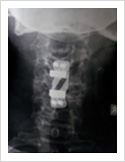
Cervical Myelopathy
Chronic ompression of the cervical spinal cord produces numbness and weakness of hands and legs, unsteady gait. If untreated, it can cause the patient bowel and bladder paralysis with inability to walk. It requires surgery in the form of decompression. If can be done from the front of the neck or from the back of the neck.
CV Junction Surgery
Junction between the head and neck is known as craniovertebral junction (CV junction). Conditions such as trauma, tumor or tuberculosis can affect CV junction causing instability, pain and paralysis. These patients may require plate and screw fixation between the skull bone and vertebra.
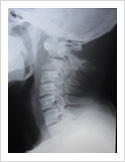
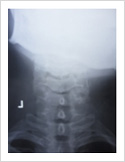
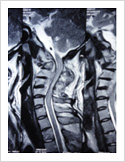
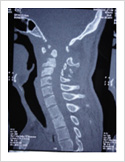
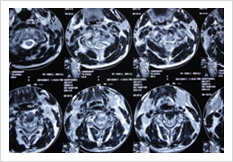
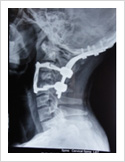
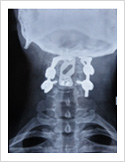

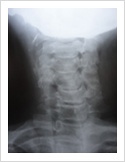
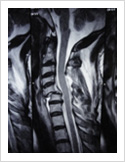
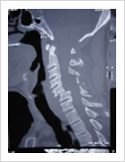
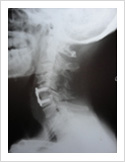
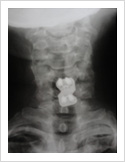
Cervical Dislocation
Thoracolumbar Trauma
Trauma can injure the spine. It can produce fractures, dislocations with or without spinal cord injury. If there is spinal cord injury, patient will have neurologic deficit. Treatment involves spinal stabilisation with or without fusion.
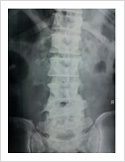
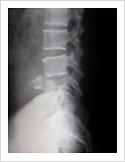
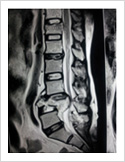
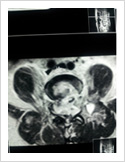
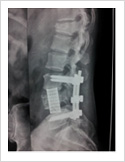
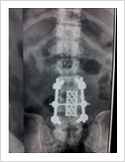
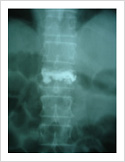
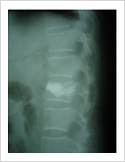
Vertebroplasty
In elderly patients with vertebra fractures due to osteoporosis, immediate pain relief is obtained with a keyhole surgery called vertebroplasty. In this procedure, bone cement is injected into the fractured vertebra using two needles. The cement hardens in 15 minutes and stabilises fractured bone. It gives immediate pain relief and patient can resume his normal duties immediately.
Lumbar Canal Stenosis
This is a condition in which there is progressive narrowing of spinal canal resulting in neurogenic claudication. Patient complains of pain in the lower limbs on walking which is relieved by rest. Diagnosis is confirmed by MRI scan. Treatment involves decompression of the spine. If there is associated instability, it requires spinal stabilisation and fusion.

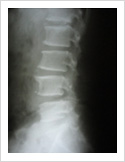
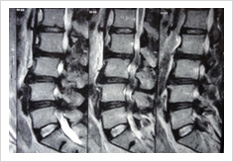
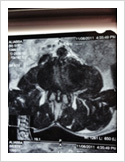
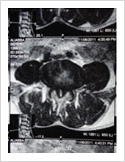
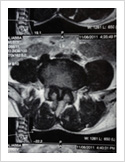
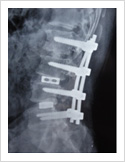
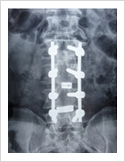

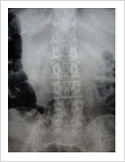
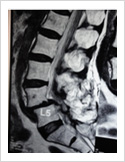
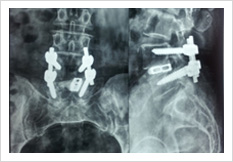
Failed Back Surgery
This is a condition in which patient who had lumbar spine surgery earlier, develops recurrent symptoms due to various causes. The causes can be infection, recurrent disc prolapse, instability, arachnoiditis, and epidural fibrosis. It is important to identify the cause for successful treatment. If there is instability/ infection/ recurrence, it may need spinal stabilisation and fusion. Other causes may need medical management.
Spondylolisthesis
This is a condition in which there is slipping of one vertebra over another. In the initial stages, it may not produce any symptoms. Later, this can produce back pain, leg pain, and neurologic deficits. It is treated by spinal stabilisation and fusion.
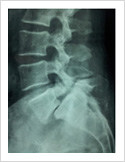
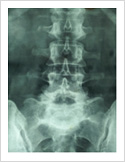
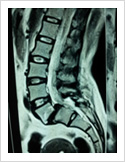
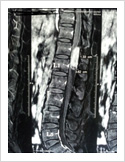
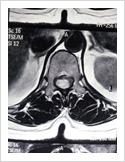
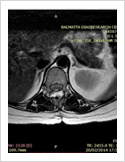
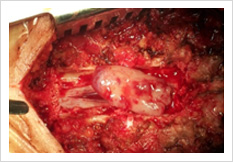
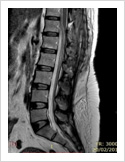
Spinal Cord Tumor
Rarely, tumours can affect the spinal cord or the nerves. If the tumor is slow growing, it may be asymptomatic for many years. Spinal tumours can produce pain, weakness or numbness of limbs and sometimes bowel or bladder paralysis.
Scoliosis Surgery
Scoliosis is a deformity of the spine where there is bending and rotation of the vertebra. The causes can be congenital, neuromuscular, degenerative, idiopathic e.t.c. Most of the idiopathic scoliosis (cause is not known) occur in children. This may be missed in the early period because patient does not have any pain or neurologic symptoms. The diagnosis is by clinical examination. If the curve exceeds more than 40 degrees, it requires surgery. Scoliosis surgery is a major spine surgery. It involves fixation of the spine with screws and hooks, correction of deformity and fusion of bones to prevent recurrent deformity.
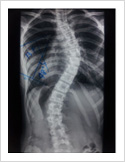
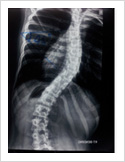
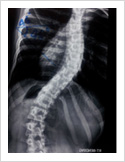
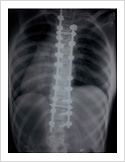
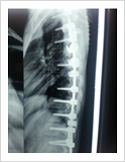
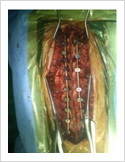

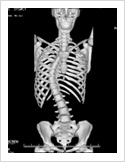
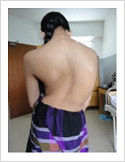
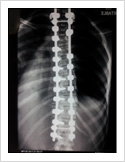
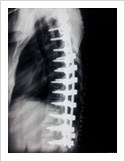
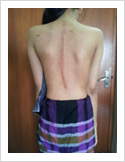
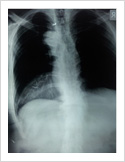
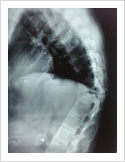
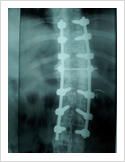
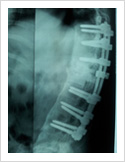
Kyphosis Correction- Spinal Osteotomy
Kyphosis is a deformity of the spine where there increased forward bending of the spine. The causes can be congenital, ankylosing spondylitis, post traumatic, infection, osteoporosis, tumors. Kyphosis correction is a challenging surgery even for experienced spine surgeons. It involves fixation with pedicle screws, osteotomy of spine and fusion.

